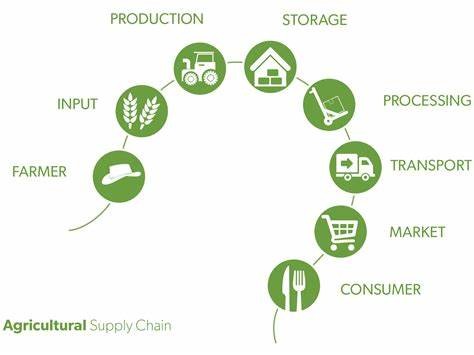
What is Importing Fruits and Vegetables Like?
The major reason for having fruits and vegetables imported is the seasonal differences between countries. Another factor is the land and soil, which caters to fruits in some countries but does not in others. For a country's growing population, it may not have enough land to grow fresh produce for all its citizens. Therefore, it is needed for the country to import fruits and vegetables from overseas. In addition to this, the preference of a country's citizens is also likely to have an effect on its import quantities.
If the people end up developing a taste for healthier and fresher food, the country will have to import all kinds of fruits and vegetables to meet its demands. Some countries in the Middle East and Europe are the largest exporters regarding fruits and vegetables. The fresh produce grown there is supplied to all parts of the world, which is a great boost for the GDP and strengthens the economy as well. Usually, importing profits leads to huge profits being made for the supplying party, as consumers are always growing in number. For example, American citizens have a year-long demand for tropical fruits that do not grow in all seasons. Some fruits in demand do not grow in the US at all. Therefore, the American importers need to supply these fruits for their citizens in large quantities.
What do Importers do?
It is important to fully understand the exact role of importers. The importer is usually a citizen of the country that the goods are being imported into. It should also be noted that the importer can either be an organization or an individual. When discussing something large-scale as fruits and vegetables, it is safe to assume that each country has an authorized importing business. The activity that goes on in these importing organizations is closely monitored by the government.
The head of the organization is responsible for carrying out all the transactions smoothly and being aware of any changes in exchange rates, import tariffs, and duty rates. It is common knowledge that if a country's imports exceed its exports, a trade deficit can occur. This is also known as a negative balance of trade. To figure out which goods will be less expensive to import, one can take a look at the tariff schedules and free-trade agreements of the country in question. For example, the free-trade agreements in the US increased drastically between 1989 to 2019. This caused the imports to cost to go up to $3.1 trillion.
What Problems Are Faced By Importers?
Managing the imports that come into a country is no easy task, in any way. The process can get quite complicated at times, as there are numerous trade laws and documents that need to be processed before goods can be imported. Before your imported goods can make it into retail shops and markets, you have to consider the numerous procedures at customs, and what requirements they need to clear through easily. The top fruits and vegetables that are imported all over the world are Bananas, Tomatoes, Pineapples, Peppers, Cucumbers, Melons, and more.
· One of the most obvious challenges that importers have to face when importing fresh produce is the items' durability. Fresh fruits and vegetables are considered perishable items and they are bound to rot and go bad within a few days of being harvested. Even though farmers have tried to breed species of fruits and vegetables that are capable of withstanding long hours and distances, the items are still not very durable. In addition to this, these different species are also less flavorful and do not contain as many nutrients. This is why they are less preferable.
· Having insufficient knowledge about the exchange rates between the two parties who are participating in imports is one of the many reasons the transactions fail. Each importing business has a budget to work around and fit in as many imports as possible. Keeping this in mind, if they do not plan ahead for any fluctuations in the exchange rates, they can be financially challenged and may have to call off the whole transaction. This can be at a great disadvantage for the country's economy. This is why it is always advisable for the importing business to check in with their bankers and find out any important predictions in the exchange rates.
· An importing individual or authorization needs to be careful and on good terms with the other country's customs officers. This also includes the custom brokers and the transportation facilities that take your imports from one place to another. Make sure you are cordial and polite enough with these figures and mark anything they tell you as important, as they are knowledgeable enough about their country's exporting businesses. Not having a good relationship with the customs department may seem like a trivial thing, but it can put serious hurdles in the way of importing goods successfully.
· Keeping track of the various documents involved in importing can be a hassle at times. This includes the commercial invoice, which is a sort of receipt, only more detailed. This invoice is between the supplier and the importing company, and it lists all the various facts, costs, fees, and numbers that are associated with the imported goods. A copy of the commercial invoice is kept with the importing party to show to the customs department. This helps customs to properly tax the items according to their weight and value. The commercial invoice also includes the addresses, names, and other means of contact of both the importing party and the supplier.
· When importing something into your company, it is crucial to be aware of the packaging, and marketing laws that are associated with fresh produce. Some countries may require you to put specific labels on their items that show where the food was grown and harvested. Other countries may have more flexible rules, but the quality of the product still matters. For example, fresh produce grown in China does not usually meet the quality standards of American citizens, which is why their items are often held back at customs and not allowed to proceed further. Importing companies have to take great caution when judging the state of the fruits and vegetables before they can agree on importing them to their countries.
· Importing parties often have to struggle with communication barriers when participating in import businesses. Some may even say that this issue is the root of all other problems associated with importing. This is because learning the other country's language is simply not enough, there are certain traditions and meanings that can not be understood by the outsider. This can cause problems as there may be too much miscommunication to negotiate terms, and state laws and rules. The importing party may misunderstand the laws and create a troublesome situation for themselves.
· Exchange rates may also pose issues for these importers in sourcing their products. It must be understood that when the demand for a currency exceeds supply, its value will rise. This is called an exchange rate appreciation because one unit of the currency will buy more units of other currencies. When a currency is appreciated, importers of foreign raw materials usually benefit from it, these include fruit and vegetable suppliers. Moreover, lower import prices will help to reduce the rate of inflation for the whole economy and all firms are likely to gain from this more stable position.
· Lastly, import organizations often have to deal with long waiting times in the business. This is because, for a country like America, or countries in Europe, there are several importing countries that are already on the wait-list to get their products across. The fruits and vegetables also take a long time to grow, ripen, and harvested. After this, considerable time goes into transporting them across several borders, and when they are finally cleared through customs and security, it may take anywhere from a few weeks to several months. It is often difficult to speed up the process in any way, as the persihable nature of fresh produce is already discussed.
·Export Fruit Trade as Key Driving Force of Agriculture Industry
· While there have been many companies coming up with solutions to solve the problems mentioned above, it is also worth looking at the key driving force behind the global fresh produce and agriculture industry. According to a 2018 FreshPlaza report, the total export trade in fresh fruit and vegetables has developed more rapidly than the total global trade in goods in the past ten years. The international trade in fresh fruit increased by an average of 2 million tonnes per year to about 80 million tonnes in the past 10 years, and the five key trade flows pegs Southeast Asia as the growth market. Mutual trade flows in Southeast Asia performed best with the largest absolute growth in global trade flows of fresh fruit to almost 8 million tonnes worth of fruit a year, as well as rapid growth of exports from North America, Latin America and the rest of the world into Southeast Asia.
·Trade Dispute: Huge Problem of Companies Doing Export Trade
· The high growth of cross border trade in the produce industry has also magnified the problems of conducting produce trade. Problems like trade disputes over food quality can cause up to 5-10% loss per container of fruit exports. Food safety issues, a rampant problem of the industry, often result in entire batches of produce being rejected or destroyed, creating millions of losses. It is no wonder that the need for supply chain and trade transparency was one of the key highlights during Produce Marketing Association (PMA)’s 2019 Tech Knowledge event to solve the “Messy Middle” of global produce supply chains.
·Supply Chain Transparency Solves The “Messy Middle”
· Supply chain transparency has been little more than a buzzword due to the overwhelming complexity of food systems. While industry giants such as Walmart, Carrefour and Nestle have started implementing traceability solutions in a bid for more transparency, it has been difficult for supply chain transparency to gain more traction throughout the industry. There are limited players that have adopted traceability solutions. This is mainly because the produce supply chain simply involves too many moving parts and stakeholders, and no one traceability solution has been able to work for all the players.
·Getting Supply Chain Transparency to Work
· For supply chain transparency to work, it is important to target the meat of the problem – getting the data from physical produce.
· What does this mean? Millions of physical cartons of fresh produce products are being moved every day, yet there has not been a way to effectively and efficiently track them, as well as easily access information related to each carton, nor prove the quality of the produce. A key obstacle would be digitalizing the produce and the carton it is packed in. Without a digital identity, it would be extremely difficult to track
· Operational aspects also need to be considered for digitalizing produce to be applicable. They include being able to efficiently capture all the digital identities of the produce and cartons as they move through packing lines on the ground so that there are minimal disruptions to existing workflows. Not all packing houses are created equal – some are highly automated, while others are still largely manual. Thus for traceability solutions to work down to the product level, it is important to cater to the needs of different produce companies.
·At the same time, digital identities need to be easily readable by all supply chain stakeholders. A good solution would be to adopt GS1 Standards for labels, a common foundation for business by uniquely identifying, accurately capturing and automatically sharing vital information about products.
·Maximizing the Data from Digital Supply Chains for Added Benefits
·At the same time, the benefits of adopting traceability technology have yet to be communicated well to fresh produce companies. Traceability alone is not enough to motivate industry players to adopt potential solutions. The ability to do branding with QR Marketing, as well as direct consumer engagement, is also highly attractive to brand owners looking to build their brands in new overseas markets. The potential to capture more personalized consumer data can let producers and retailers understand more about their consumers and facilitate the matching of supply and demand on the consumer level.
·Another advantage of digitalizing supply chains would be trade financing – Produce companies, traditionally, never had trade financing opportunities as many financial institutions often consider the perishable industry too complex, and too high a risk. With digitalization and easily accessible supply chain information, financial institutions may be more keen to provide trade financing opportunities to fresh produce companies.
www.e-fresco.io
 English
English